|
Bilateral and multilateral cooperation activities on environmental matters, at the European level, of international bodies and agencies and with developing countries, are central to the "International actions for the ecological transition and Sustainable Development" (established by the Act of address for the 2023 political priorities for the three year period 2023-2025 of the Ministry of the Environment and Energy Security).
These actions are to be seen within a framework of environmental commitments signed by Italy during global events:
- Convention on Biological Diversity – CBD, (Rio, December 1993), COP15 (December 2022)
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification – UNCCD, (1994), COP15 (May 2022)
- 2030 Agenda 2030 for sustainable development, (New York, September 2015)
- Addis Ababa Action Program, (Addis Ababa, July 2015)
- Paris Agreement (COP 21) (Paris, December 2015, within the 21st Conference of the Parties to the UNFCCC, from over one hundred and seventy countries, each has expressed its own goals through the Nationally Determined Contributions, NDCs)
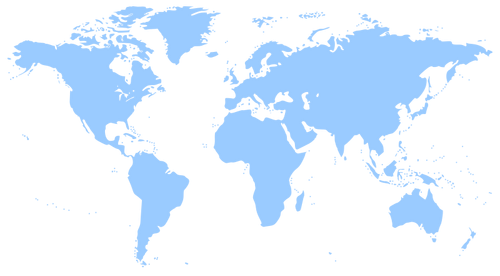
To date, MASE's bilateral cooperation has 37 active cooperation agreements and 27 agreements under renegotiation and new negotiations, for a total of 81 countries involved. The 46 currently active projects commit a total of resources, donated by the Ministry, for over 80 million Euros, and pursue the Sustainable Development Goals, (SDGs), outlined by the 2030 Agenda. Among these, in particular: goal 6 "Clean water and sanitation", goal 7 "Affordable and clean energy", goal 13 "Climate action", goal 14 "Life below water" and goal 15 "Life on land".
|
*The 11 signatures of the CARICOM countries are considered Data up to June 2024
The signing of a Protocol of Understanding, or Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), with a foreign Counterparty, is the framework in which our bilateral cooperation fits. Within it, projects are approved and implemented in the various countries.
After negotiation between the parties, the Memorandum of Understanding must receive the authorization for signature by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation, (MAECI). At the internal procedural level, the MoU provides for the establishment of a Joint Committee, (JC), made up of representatives of MASE and the Counterparty. The Joint Committee (JC) is the decision-making, control and monitoring body of the MoU itself and meets at least once a year. The JC approves the procedural documents, the projects, the budget and the medium-term Work Plan and for each project.
At a financial level, the project budget provides for a grant from MASE, which can fully cover the costs, or provide for the participation of a co-financer, (e.g. UNDP, ENEA, the Counterparty itself). The resources are transferred on the basis of the tranches established, the progress and the technical-financial reports presented for evaluation and approval by the donors.
|
| Countries with ongoing agreements |
| Africa: Botswana, Eswatini (Swaziland), Ethiopia, Kenya, Lesotho, Morocco, Congo Democratic Republic, Rwanda, South Africa, Tunisia, Uganda, Zambia |
| Asia: China, India, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Vietnam |
| Middle East: United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Kurdistan (Iraq), Lebanon, Palestine, Turkey |
| Caucasus: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia |
| Europe: Albania, Russian Federation, Montenegro, Serbia, Ukraine |
| America: Argentina, Chile, Costa Rica, Cuba, Mexico, Paraguay, Peru, Dominican Republic |
| Small Island Developing States (SIDS): Small Pacific developing island states (14 countries: Cook Islands, Fiji, Kiribati, Micronesia, Marshall Islands, Nauru, Niue, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu and Vanuatu); Caricom (9 countries: Antigua and Barbuda, Saint Lucia, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Belize, Dominica, Guyana, SaintVincent and the Grenadines, Suriname and Haiti); Maldives, São Tomé and Príncipe, Seychelles, Union of the Comoros, Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS) |
| Countries with agreements under negotiation |
| Africa: Cameroon, Mauritania, Mozambique |
| Asia: Kyrgyzstan |
| Middle East: Iraq, Kuwait |
| Europe: North Macedonia, Moldova |
| Small Island Developing States (SIDS): Mauritius |
| Countries with terminated agreements |
| Africa: Egypt, Djibouti, Mali, Sudan |
| Asia: Iran, Qatar, Kazakhstan |
| America: Nevada |
| Partnership: Lake Chad Basin Commission (Niger, Nigeria, Camerun, Chad); Redd+ (Dominican Republic, Ghana, Panama, Papua New Guinea) |